CRATER LAKE
Crater Lake Project Overview
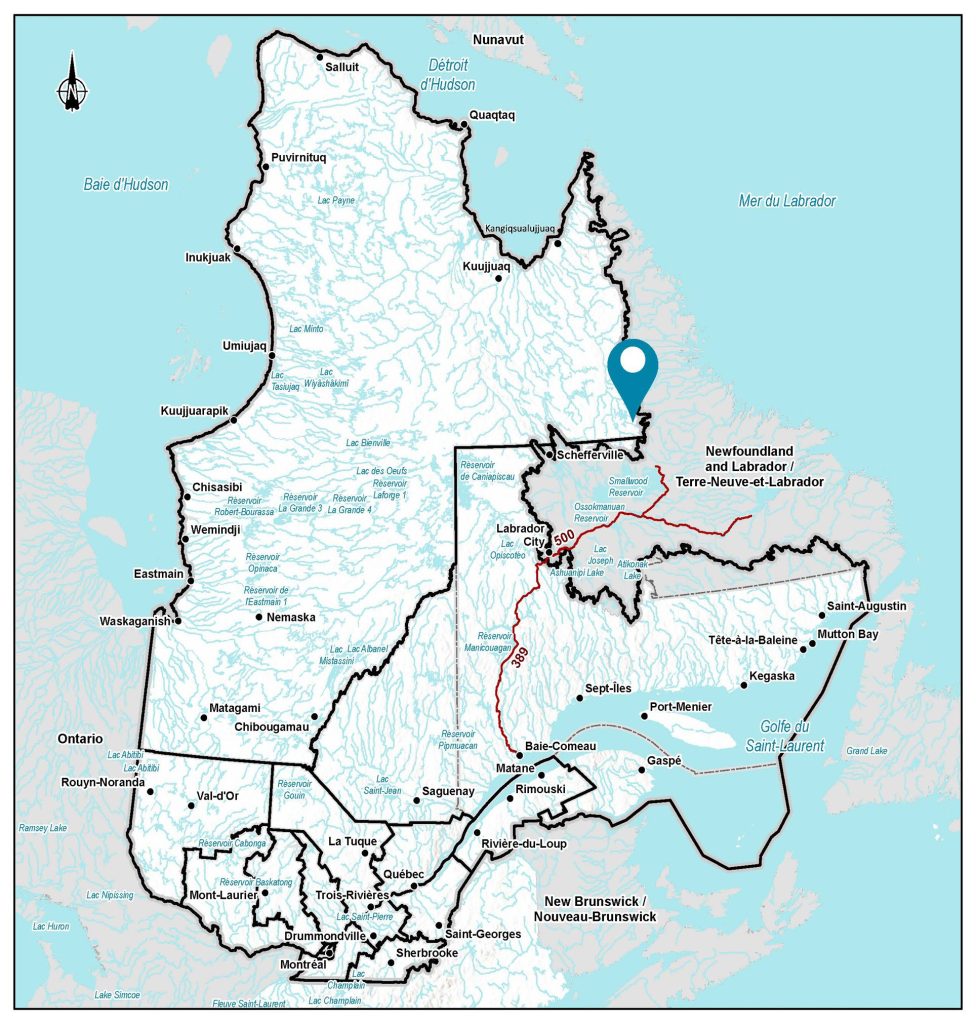
Wholly owned by Scandium Canada Ltd., the Crater Lake Project is the North America’s largest primary source of scandium. Located in Nunavik, Quebec, approximately 200 km northeast of Schefferville, the site is accessible by plane or helicopter. The property consists of 96 contiguous exclusive exploration rights covering a total area of 47 km².
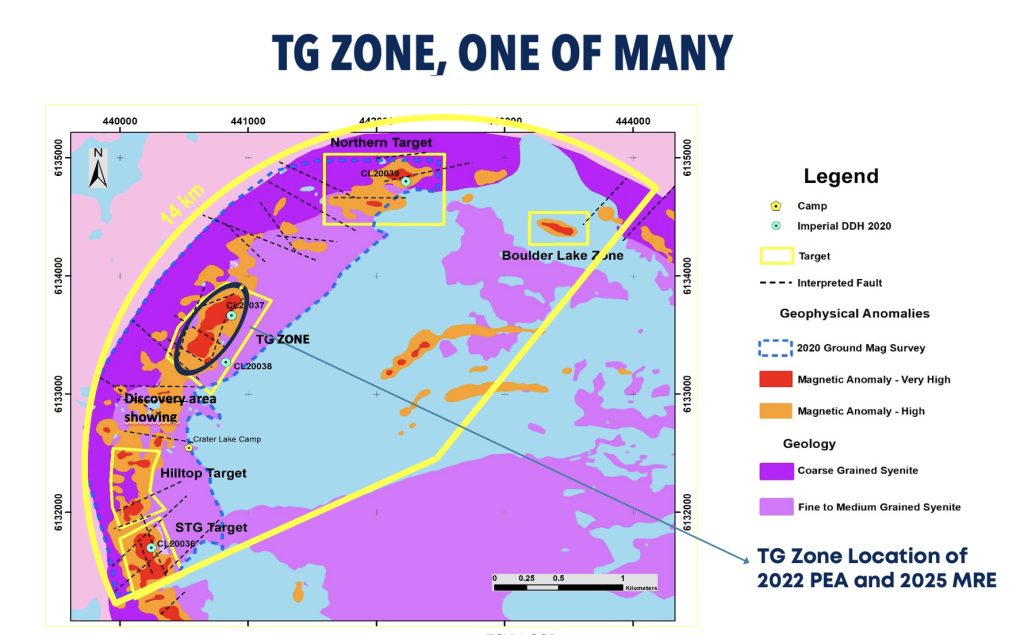
Since 2010, exploration on the Crater Lake project has been more focussed on its scandium potential, leading to the identification of at least 5 main zones of interest that returned good grades. The latest 2024 diamond drilling campaign led to a updated 43-101 compliant mineral resources estimates on the TG Zone, and will be the basis of a pre-feasibility study.
History
Crater lake TG Zone is positionned to become a strategic asset for North American aluminum-scandium alloys supply chains, particularly in the aerospace, transportation, and energy sectors.
History
Crater lake TG Zone is positionned to become a strategic asset for North American aluminum-scandium alloys supply chains, particularly in the aerospace, transportation, and energy sectors.
Quest Rare Minerals Inc. acquired the property
Quest Rare Minerals did airborne geophysical surveys, structural mapping, surface sampling and exploration diamond drilling.
Scandium Canada acquired the property and begins diamond drilling campaigns, confirming scandium-rich mineralization in the TG Zone.
First NI 43-101 compliant mineral resource estimate is published.
Laboratory metallurgical testing confirms feasibility of producing scandium concentrate from Crater Lake ore.
TG Deposit - 43-101 Compliant preliminary economic assessment
Scandium Canada announces the update of its mineral resource estimate for the TG Zone, located on the Crater Lake project.
A Pre-Development Agreement is signed with the Naskapi Nation of Kawawachikamach, laying the groundwork for long-term collaboration.
Definition drilling confirmed an extension of 250 meters of the TG zone.
A new mineral resource estimate.
500kg metallurgical pilot test for Crater Lake scandium project completed
Naskapi Nation of Kawawachikamach invests in Scandium Canada
Geology
The project is situated in the Churchill geological province, within the Mistastin Batholith, which spans pproximately 5,000 km². The local geology is dominated by massive syenites and ferrosyenitic units rich in ferromagnesian minerals such as fayalite, hedenbergite, and ferropargasite. These formations are associated with concentric magnetic anomalies, suggesting a ring structure linked to a caldera collapse.


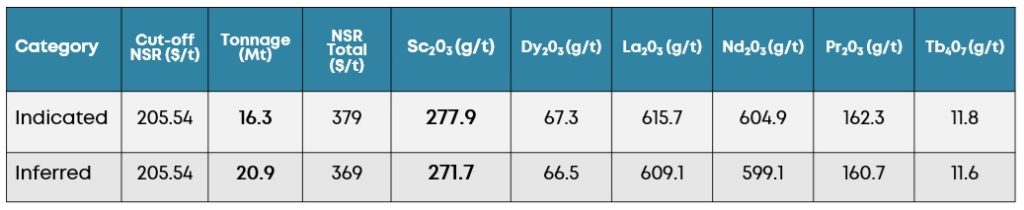
Mineral Resource estimate (April 2025)
The latest NI 43-101 compliant mineral resource estimate, prepared by Norda Stelo Inc. confirms the extension of the TG Zone to over 550m. Mineralization remains open laterally and at depth, offering additional potential for expansion.
RESOURCE ESTIMATE TABLE
Next Steps
- Scandium Canada is advancing work toward completing a Pre-Feasibility Study expected in June 2026.
- Evaluation of two potential permanent access roads. A final decision should be made before the end of 2025.
- In parallel, discussions are underway with strategic investors and potential buyers of aluminum-scandium alloys.